Sunday, 10 November 2013
Teaching the kids to retrocode
To get this I learned to program the BBC micro computer. For those who don't know here's the summary:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BBC_Micro Its 1980's home computer. It has 8 bit CPU with 32KB of memory and runs about 2MHz. Compare this to modern PCs which have 4GB of Memory (x125000 as much) and run at 4GHz (x2000 times as fast). Did I mention that you have to plug them into a TV to make them work and load and save their programs to a audio cassette?
Anyway I was down in Singapore Science Centre, today & what did I find but:
Instantly, I grabbed the kids & pulled them in.
After they had finished playing pacman using pieces of fruit (I know it sounds weird, it was a demo of using conductivity). I managed to spot a spare computer and had them sitting down and play in grannies garden (those who know it love this game).
I then handed them a handy programming sheet and a got them onto it. It was a little funny with the locals asking me for help, (they assumed I was one of the organisers), but I didn't mind I was back into my environment and remembering all the strange quirks of how a BBC was to program. The tutorials were very good stuff, only 15 minutes or so to type in (depending upon your keyboard skills).
Here were the results:
Did they enjoy it, YES. Did I enjoy it? EVEN MORE!
My next thoughts are, can I build some simple graphical tutorials (like the ones the kids did), which can be typed in so quickly and easily? It will probably by Python on a Raspberry Pi. But I need to put my thinking cap on a bit to look at this.
TTFN,
Mark
Thursday, 26 September 2013
The Programmers RPG
Its a silly 5-10 minute game which I built as final assignment for a class I was taking on Unity 3D. After I finished it, I decided, ‘let try to publish it on Kongregate, the worst they can do is laugh at it and reject it’, so I did.
Well, I put it up, it was accepted instantly & is still on the main page (4 days after being put up).
That’s kind of cool, but I’m not really impressed with this game. What I am impressed with was the way I got a reasonable RPG system to work & that’s what I’m going to be talking about in these posts.
The Basics:
What things are the “must have” for RPG’s? Here are the main bits I added.- Dialog system (PC’s talking to NPC’s)
- Message display (for any other stuff)
- Quests/Missions
- Combat (but my combat system wasn’t very good, so I won’t talk on it much)
There are also some other “must have’s” for RPG’s which I didn’t add:
- Levels & XP
- Items & Inventory systems
- Saving games
There were also a lot of over standard game conventions dropped in this game, which I might cover later:
- Health bars (2D & 3D)
- Arrow’s showing you where to go
- Knockback
- Treasure springing from the chest & being attracted to the player
- Respawns
- Mouse look with the zoom in & out
- Things flashing for a bit & vanishing
But lets get back to the main bit, the quests.
Dialog system:
For those not sure, go over to google & type ‘RPG dialog box’. The hoards of pictures show a very clear idea of what we want: the text appearing letter by letter, faster if you hold the button, often with pictures of the character(s) talking.So here is roughly what the code looked like:
public class RpgDialog : MonoBehaviour
{
public GUISkin skin;
public float textRate = 2; // how fast the text appears
public AudioClip tickSound; // audio
public int border=5, height=100; // size of dialog
float textCounter = 0;
Texture2D leftImage, rightImage; // images
string theText = null; // the text (null means hidden)
Rect mainRect; // rectangle for box
public bool Finished { get { return theText==null; } }
public void Show(string txt, Texture2D left, Texture2D right)
{
theText = txt;
leftImage = left;
rightImage = right;
textCounter = 0;
}
public void Hide()
{
theText=null;
}
void Start()
{
// if sound add the audio
if (tickSound!=null)
{
AudioSource aud=gameObject.AddComponent<AudioSource>();
aud.clip=tickSound;
}
// put the box at bottom of screen
mainRect = new Rect(border, Screen.width-border-height, Screen.width - border*2, height);
}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update ()
{
if (Finished) return;
int oldCounter=Mathf.FloorToInt(textCounter); // for use later in audio
if (Input.anyKey) // any key makes it faster
textCounter += Time.deltaTime * textRate*10;
else
textCounter += Time.deltaTime * textRate;
// tick sound when displaying
if (tickSound!=null && textCounter < theText.Length)
{
if (oldCounter!=Mathf.FloorToInt(textCounter)) // if new text
{
audio.clip=tickSound; // make sure it stays as a tick
audio.Play();
}
}
// if finished & space bar
if (textCounter >= theText.Length)
{
if (Input.GetKeyDown(KeyCode.Space))
Hide();
}
}
void OnGUI()
{
if (Finished) return;
// set the skin
GUISkin oldskin = GUI.skin;
GUI.skin = skin;
GUI.Box(mainRect, ""); // draw the box
// inner rect is where we must display the text
Rect innerRect = GuiUtils.InflateRect(mainRect, -border, -border);
// draw images as needed
if (leftImage != null)
{
GUI.DrawTexture(new Rect(innerRect.x + border, innerRect.y + (innerRect.height - leftImage.height) / 2, leftImage.width, leftImage.height), leftImage);
innerRect.x += leftImage.width + border * 2;
innerRect.width -= leftImage.width + border * 2;
}
if (rightImage != null)
{
GUI.DrawTexture(new Rect(innerRect.xMax - rightImage.height - border, innerRect.y + (innerRect.height - rightImage.height) / 2, rightImage.width, rightImage.height), rightImage);
innerRect.width -= rightImage.width + border * 2;
}
// draw the text
if (theText != null)
{
string s = theText;
if ((int)textCounter < theText.Length)
s = theText.Substring(0, (int)textCounter);
GUI.Label(innerRect, s);
}
// restore old skin
GUI.skin = oldskin;
}
}
The actual code had a little more than this, it also had a fade out routine to make it look a little nicer.
Notice the use of the GUISkin. This allows me to customise the appearance of the dialog box, setting the font, text colour & background.
To make the dialog work I had a single game object, tagged as game controller and with this behaviour added.
Then the code to make this dialog appear looks like this:
// get the dialog
RpgDialog dialog= GameObject.FindGameObjectWithTag("GameController") . GetComponent< RpgDialog>();
dialog.Show(“hello world”,null,null);
I will get on to how to stream all the dialogs together later.
Status message system:
This is not always found in RPG’s, its also very common on multiplayer games. Its the one which appears and says general information, without stopping the gameplay.In essence its just a simple GUI routine with a list of strings to hold. The only clever bits, were just a timer to automatically move the text up once in a while & finding out how much text to hold. Here is the code:
public class MessageDisplay : MonoBehaviour {
public float height = 100;
public float border = 5;
public float advanceDelay = 5;
Rect mainRect;
List<string> messages = new List<string>();
float nextAdvance = float.MaxValue;
public void Clear()
{
for(int i=0;i<messages.Count;i++)
messages[i]="";
}
public void ShowMessage(string msg)
{
// remove one, add one
messages.RemoveAt(0);
messages.Add(msg);
nextAdvance=Time.time+advanceDelay; // in X seconds remove a message
}
// Use this for initialization
void Start ()
{
// put the box at bottom of screen
mainRect = new Rect(border, Screen.width-border-height, Screen.width - border*2, height);
float lineHeight = skin.label.CalcSize(new GUIContent("W")).y;
int maxLines = Mathf.FloorToInt(mainRect.height / lineHeight);
// setup it with empties
for (int i = 0; i < maxLines; i++)
messages.Add("");
}
// Update is called once per frame
void OnGUI()
{
// don’t show if the dialog is active
if (!GetComponent<RpgDialog>().Finished()) return;
// clear the screen after a while
if (Time.time >= nextAdvance)
{
ShowMessage(""); // adds a blank
// which will reset the timer too
}
string s = "";
for (int i = 0; i < messages.Count; i++)
{
s += messages[i];
s += "\n";
}
GUI.Label(mainRect, s, skin.label);
}
}
To use this, just put the component on the same game controller object. And access it the same way. To stop the message display interfering with the rpg dialog, there is a simple check to spot if its in use & then don’t display the messages.Again to use it is simple, just get a reference to the script & call a method or two.
// get the message
MessageDisplay message= GameObject.FindGameObjectWithTag("GameController").GetComponent<MessageDisplay>();
message.ShowMessage(“its a message”);
The quest system:
- Use of Unity’s resources
- Coroutines (this is the main one)
- Use of static variables (I wrote an article on this before http://codethegame.blogspot.sg/2012/02/static-variables-in-classes-and-games.html)
When the player walks up to the NPC they touch a trigger, the script on the old man reacts to this and checks the flags.
The flags are a collection of static variables which store which quests/missions have been performed or not.
If the correct flags are set, the NPC’s script will attach the quest script to the game controller.
The quest script is basically a big coroutine which will trigger the various other scripts we just wrote (the dialog and message) and activate them.
public class QuestTrigger : MonoBehaviour {
public string questName;
void OnTriggerEnter(Collider other)
{
if (other.tag == "Player")
{
// add quest to the main RPG & this destroy myself to stop muliple triggers
GameObject rpg=GameObject.FindGameObjectWithTag("GameController");
rpg.AddComponent(questName);
Destroy(this);
}
}
}
Lets look at a silly quest. These can be written in C# or Javascript. I found Javascript to be simpler to work with because of the auto wrapping of coroutines, but I give them both as examples.
A C# quest:
public class qst_start : MonoBehaviour {
// Use this for initialization
void Start ()
{
StartCoroutine(DoQuest()); // start a coroutine
}
// all C# coroutines must return a IEnumerator
IEnumerator DoQuest()
{
// load the resource
Texture2D portrait=(Texture2D)Resources.Load("portrait");
// get the dialog box
RpgDialog dialog= GameObject.FindGameObjectWithTag("GameController").GetComponent< RpgDialog>();
// show the dialog and wait for it to close
dialog.Show("<Yawn>\nThat was a good nap", portrait, null);
while (!dialog.Finished()) yield 0;
dialog.Show("<Looks Around>\nErr", portrait, null);
while (!dialog.Finished()) yield 0;
dialog.Show("Where am I?", portrait, portrait, null);
while (!dialog.Finished()) yield 0;
dialog.Show("I don't remember drinking *that* much beer", portrait, null);
while (!dialog.Finished()) yield 0;
// PS if any of the functions called from here yield anything,
// you cannot call them directly, but must StartCoroutine(), them
// and so our adventure continues:
// done: now exit
Destroy(this); // remove myself
yield return 0;
}
}
A Javascript quest:
function Start ()
{
// in JS: you don't need the StartCoroutine, only the yield
var portrait:Texture2D=Resources.Load("portrait") as Texture2D;
var oldport:Texture2D=Resources.Load("port_oldman") as Texture2D;
Dialog("Greetings mighty warrior",null,oldport);
Dialog("Do you have the key?",null,oldport);
if (RPG.has_key==true) // check the static variables
{
Dialog("Yes here is is",portrait,null);
// etc,etc,etc
}
else
{
Dialog("Err, not yet ",portrait,null);
// etc,etc,etc
}
}
// don’t need to do anything complex for a coroutine in JS
function Dialog(txt:string, left:Texture2D, right:Texture2D)
{
var dialog: RpgDialog=GameObject.FindGameObjectWithTag("GameController").GetComponent("RpgDialog");
dialog.Show(txt,left,right);
while (!dialog.Finished()) yield 0;
}
Conclusion:
Thats the heart of the quests systems, the coroutines turned out to seriously simplify the work. My original version had its own mini scripting engine, but was just so much work to do.To really get it working well I would need to design how to manage the saving on game (probably at save points) and how to manage the coroutines between loading & saving.
Later I will write a bit more on the other features, but this is the most complex bit.
I hope that it helps some of you think on this.
Happy coding,
Mark
Sunday, 15 September 2013
Visual Basic and Serial Ports
After asking him I realised that he was still using VB 6 (which was a 1990's application). So I decided to put a morning aside to testing Visual Basic on Windows 7, and in particular getting the serial port code working.
So lets get to it!
1. Install VB.net
I'm using the 2010 express version, but other versions should be quite similar.A quick trip to the MS website
With the usual setup:
Its a 60MB download (not too bad)
And we are ready to go.
2. Start new project
3. Design the form
Make sure you add a serial port component from the toolboxMy form looked like this (see the serial port down at the bottom):
4. Add the code
The connection & sending was dead easy.Private Sub btnConnect_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnConnect.Click
SerialPort1.Close() ' just in case
' setup serial port
SerialPort1.PortName = txtPort.Text
SerialPort1.BaudRate = 9600
SerialPort1.Open()
End Sub
Private Sub BtnStop_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles BtnStop.Click
SerialPort1.Write("0")
End Sub
Private Sub btnGo_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnGo.Click
SerialPort1.Write("1")
End Sub
If you get any blue underlining, it just means its missing a library, right click on the offending item & import the library.
5. Add the receiving code
First task, select the serial port & get up its properties. Then you need to give the name of a function to be called when there is data waiting to be received.You then double click on the item & it brings you to the code editor & you can just type in your code:
Private Sub OnDataIn(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.IO.Ports.SerialDataReceivedEventArgs) Handles SerialPort1.DataReceived Dim sp As SerialPort = CType(sender, SerialPort) Dim indata As String = sp.ReadExisting() System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine(indata) End Sub
This ALMOST works, but often I found that VB would be reading too fast & not get the entire line of data, just part of it
So a small change to the code & we are good
Private Sub OnDataIn(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.IO.Ports.SerialDataReceivedEventArgs) Handles SerialPort1.DataReceived Dim sp As SerialPort = CType(sender, SerialPort) ' note: ReadExisting() will only read what is in the buffer right now ' which means you might get only half the message & have to reassemble it ' Its far easier to use ReadLine() which will block until the whole line is in 'Dim indata As String = sp.ReadExisting() Dim indata As String = sp.ReadLine() System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine(indata) End Sub
6. Deal with the dragons
So last task is just take this text and update the UI. Simple, Right? Wrong!Errr....
Lets try and address this one
To keep an eye on the serial port, VB runs a thread. But it’s not the same thread that is running the rest of the UI and all our other code.
Thread B is not allowed to access the UI stuff which is owned by thread A, because it’s basically very dangerous to let two threads play around with the same things at the same time.
7. Solving the problem with an invoke
I tracked down a fairly simple piece of code to get around this issue from http://www.dreamincode.net/forums/blog/143/entry-2337-handling-the-dreaded-cross-thread-exception/It looked like this:
' this delegate will help us later
' for those from a C/C++ background, think 'function pointer'
Delegate Sub ThreadSafeDelegate(ByVal ctrl As Control, ByVal str As String)
'The method with the delegate signature
Private Sub ChangeText(ByVal ctrl As Control, ByVal str As String)
If ctrl.InvokeRequired Then
ctrl.Invoke(New ThreadSafeDelegate(AddressOf ChangeText), New Object() {ctrl, str})
Else
ctrl.Text = str
End If
End Sub
What its doing, is if the function if called from thread B, the thread invokes the function (it puts the function & all the arguments in a safe place). Then later when thread A comes by, it notices the function needs to be called & calls it.
I then added my version to do the job I really wanted
Private Sub AppendText(ByVal ctrl As Control, ByVal str As String)
' if not thread safe, recall this function
If ctrl.InvokeRequired Then
ctrl.Invoke(New ThreadSafeDelegate(AddressOf AppendText), New Object() {ctrl, str})
Return
End If
' do the real work
Dim lb As ListBox = CType(ctrl, ListBox) 'get the list box
If lb.Items.Count >= 10 Then ' if its too ful remove the old stuff
lb.Items.RemoveAt(0)
End If
lb.Items.Add(str) ' add the new stuff
End Sub
And my receive code works just fine now
Private Sub OnDataIn(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.IO.Ports.SerialDataReceivedEventArgs) Handles SerialPort1.DataReceived Dim sp As SerialPort = CType(sender, SerialPort) Dim indata As String = sp.ReadLine() System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine(indata) 'lstDataIn.Items.Add(indata) AppendText(lstDataIn, indata) ' thread save version End Sub
Conclusion:
Apart from the thread safe issue, this was so easy. But then VB was always designed for a quick UI hackup. All this work took less than 2 hours (including the time to overcome the dragon). Having to add this extra thread code might make it a little harder, but VB.Net seems to be able to still deliver the quick prototypes that VB 6 did 20 years ago.This is not the only way to some this problem. I could have done all this with C# as well, it would probably have been the same thing, with the same cross thread issue as well. But today was VB’s day.
Happy coding,
Mark
Friday, 12 July 2013
Game Programming Essentials: Groups of Objects
If I remember on some of my very old code, I used to have:
int ex1,ey1, ex2,ey2, ex3,ey3; // locations for each enemy
A say ‘should’ because I still see assignments which are handed in which have the “ex1,ey1,ex2,ey2” code in them. These are the ones which are usually awful code, and get very little marks.
There is no hard & fast rule for how to design your Sprite class, but here are the things that I expect to see:
- Position (must have)
- Update & Draw function (must have)
- IsAlive flag or a life variable (must have, more on that later)
- Rotation, velocity, acceleration variables (good to have, more on those later)
Note:
No amount of tutorials can cover every language/ game engine. As I mentioned at the beginning this is general concepts. So expect to have to do quite a bit of reading up to match this to your engine. This set works will for XNA & C++, but might not for your engine.
Simple example: a starfield
class Star: Sprite{
void Update(float dt)
{
const Vector2 VELOCITY=new Vector2(-100,0);
this.Pos += VELOCITY * dt; // move it
// deal with off screen
if (this.Pos.x <0) this.Pos.x+=640; // wrap around
}
}
List<Star> stars=new List<Stars>();
...
This is a simple example for a bunch of stars all going in the same direction & a simple wrap around routine to spot when they moved off the screen & put them on the other side.Idiot Warning:
DO NOT COPY THIS CODE IN AND EXPECT IT TO WORK!
We are covering concepts, not exact code. So you will need to adapt the code to you individual language/game engine.
Sharing Variables: Introducing statics
This starfield code is fine, but what happens if we wanted to change the speed of the starfield? Answer: we cannot! Its hard coded into the class. Many times, that’s fine, but sometimes it might not be. For example, what it you wanted the stars to move faster/slower when the player speeds up/slows down. What about if the player starts flying upwards?So let’s think of an alternative.
- Add a public Vector2 Velocity to the Star class, then each star could move at its own speed
- Add a public static Vector2 Velocity to the Star class, then all stars could move at the same speed
Now both of these options are good & valid. The solution is should we use? Answer, depends upon your real needs. Remember these posts are about general concepts, not specific solutions. If there was one fix-all solution, I will tell you. But there isn’t. Let’s look at this graphically, it might be a bit clearer:
As you can see: on both cases the star has a position attribute. But in option 2, there is only one velocity attribute which is ‘shared’, while in option 1, each has its own velocity.
For this particular case, I feel that option 2 (the static) is probably more suitable, as this is a single variable to control the movement of all stars at the same time.
So now its just a matter of getting your programming manual & looking up how to implement a static variable in the desired programming language. Here in pseudo C# is looks like this:
class Star: Sprite
{
public static Vector2 Velocity=new Vector2(-100,0);
void Update(float dt)
{
this.Pos += Velocity * dt; // move it
// deal with off screen
if (this.Pos.x <0) this.Pos.x+=640; // if off left: wrap around
// will need to add in the other cases (right, top & bottom)
}
}
Collisions & Destructions (Attempt1)
Next item on our topic list is a common topic, collisions & destroying things. We are going to start with a simple concept, space invaders:In this case, we will need a list of invaders and a list of bullets (player shots). I’m going to also assume a list of list of explosions which will nicely animate.
List<Invader> invaders=new List<Invader>(); List<Bullet> bullets=new List<Bullet>(); List<Explosion> explosions=new List<Explosion>();
Lets tackle the most complex bit first, the collisions:
Collisions Done Badly
At first this might seem like a good idea:for(int e=0; e< invaders.length; e++)
{
for(int b=0; b< bullets.length; b++)
{
if (bullets[b].CollidesWith(invaders[e])) // bullet hits enemy
{
createExplosion(invaders[e].position); // big explosion
invaders.removeAt(e); // remove the enemy
bullets.removeAt(b); // remove the bullet
}
}
}
Well, no its not, this code will probably crash within the first 30 minutes of testing. Let me give you an example:
- Assume 10 enemies & 5 bullets.
- The code loops through checking each invader against each enemy
- This cycle, bullet 0 hits invader 9, the explosion is created
- The code then removes bullet 0, since its an array, all the other bullets are moved up
- The code then removes invader 9, the invaders array is now reduced to 9 items long
- The cycle now continues to check seeing if bullets 1,2,3 hit enemy 9
- BUT: If didn’t check one of the bullets (the one in slot 1, since it got moves to slot 0)
- AND: it crashes since there is no enemy 9 anymore as the enemies are 0..8
You can try thinking some creative solutions to this problem. But the bottom line is this.
If you start adding or removing object from an array while you are looping over the array, sooner or later it will break.This is a well known programming topic: a quick google on “removing objects from a collection while iterating through it” will give you a lot of hits and a lot of ideas. But rather than try to fix it, let me present you with a different way to approach the problem.
Detour: Object Pool
In our space invaders game, how about we create up the array of 40 or so invaders we need at the start of the game. While we play the game if an invader gets killed, we just set a ‘dead’ flag on the enemy, but leave it in the array. When moving invaders we skip the dead ones & obviously we don’t draw them either. However when the next level begins, or the game restarts, we just need to go through the array cancelling all the invader’s ‘dead’ flags.
In our space invaders game, they invaders can only have a maximum of 3 bombs on the screen at once (an arbitrary limit). So we have an array with 3 bomb sprites in it. Each bomb again has this ‘dead’ flag, and at first, all bombs are marked as being ‘dead’.
Each time an invader decides it wants to drop a bomb: it checks the bomb sprite array to see if there are any bombs marked as ‘dead’. If it finds one, it sets the bombs location just below itself and marks the bomb as not ‘dead’. If there are no spare bombs, the invader will have to not drop the bomb yet.
The live bombs will drop down and once it hits the ground it marks itself as ‘dead’ and wait to be reused.
Technical Note:
In XNA on the Xbox 360 and the Window Phone and on many other mobile devices there are often lots of warnings about allocating/deallocating too much memory, as the garbage collectors are get overloaded quite quickly. Therefore having an object pool helps a lot.
And even if you are programming in C++, by not continually new-ing and delete-ing objects you save yourself a lot of pointer headaches by using an object pool.
Collisions & Destructions (Attempt2)
for(int e=0; e< invaders.length; e++)
{
if (!invaders[e].isAlive) continue; // ignore dead invader
for(int b=0; b< bullets.length; b++)
{
if (!bullets[b].isAlive) continue; // ignore dead bullets
if (bullets[b].CollidesWith(invaders[e])) // bullet hits enemy
{
createExplosion(invaders[e].position); // big explosion
invaders[e].isAlive=false; // enemy is dead
bullets[b].isAlive=false; // bullet is dead too
}
}
}
Note on naming:
Do you notice that I named my loop variables e and b, not x,y or i,j?
There is a simple reason for this. What happens if I try accessing bullets[e]?
Answer: it crashes quite quickly. There are probably only a few bullets in the array, but e was used to index the invaders & probably goes up to 40. Therefore in this case, I always use a clear loop variable name so I know which is which.
Alternatively you can use an iterator or a foreach, if your programming language supports it.
Other odds & ends
- Keep your eyes open for common sprite attributes & specific sprite attributes
- In my examples above: position & isAlive are common to all
- As it the CollidesWith() function
- But the Velocity attribute might or might not be a common
- Think carefully before adding to the base class, but go ahead and add new stuff to the derived class
- Sometimes I see students adding strange features to the base class, because they don’t know how to use the derived class or manage up-casting & down-casting. (If you don’t know what that means, do look it up)
- My example above ran with a single Boolean for isAlive, but it could so easily have been an integer variable:
class Sprite
{
int life;
bool isAlive(){return life>0;}
void Destroy(){life=0;}
void Damage(int amount){life-=amount;}
...
}
- Then we can have the invader injured by a bullet using:
if (bullets[b].CollidesWith(invaders[e])) // bullet hits enemy
{
invaders[e].Damage(5); // damage invader
bullets[b].Destroy(); // remove bullet
if (!invaders[e].isAlive()) // its just died
createExplosion(invaders[e].position); // big explosion
}
- Be careful with object pool sizes:
- The more objects you put in the pool, the more you can have active at once. But the more memory it takes, (having a large pool of dead objects does take a little CPU, but not much)
- Ask yourself, do you really need 1000 enemies ‘just in case’?
- Also remember that it is possible that all pool members might be busy, so always check for it. Eg.
void createExplosion(Vector2 position) // big explosion
{
// look for spare explosion
Sprite spare=null;
foreach(Sprite s in explosions)
{
if (!s.isAlive)
{
spare=s;
break;
}
}
// VITAL: check to make sure there is a spare
if (spare==null) return; // no spares
... // do whatever you need
- Clever programmers will spot the foreach loop & recognise that it could be moved to a function
- Really clever programmers will realise it can be make into a template/generic function
- Learn how to tell when it’s better to use two lists of sprites, or combine them into a single list of sprites.
- I don’t have a good ruling on this one. Having a list of different types of sprites is what polymorphism is all about isn’t it? The trouble is that taken too far can cause so much complexity, that it’s easier to separate them.
- Generally though, it often keep my sprites apart
Conclusion
Monday, 8 July 2013
Game Programming Essentials: Motion of Objects
First topic: making stuff move, obvious stuff.
When I first started making stuff move I tried the following:
for(int x=0;x<640;x+=10)
draw_enemy(x,20);
But it quickly became obvious that this kind of idea won’t work.
Quite quickly you find out about the game loop:
while(!game_over){move_everything();
draw_everything();
}
Which clears matters up and you figure out what you need to do.
Tip: |
Simple position based movement
So we usually end up with some code to move our player which looks a little like this:
Sprite player;
...
const float SPEED=10;
if (KeyDown(LEFT))player.x-=SPEED;
if (KeyDown(RIGHT))player.x+=SPEED;
if (KeyDown(UP))player.y-=SPEED;
if (KeyDown(DOWN))player.y+=SPEED;
And this works just fine.
Tip: Dealing with variable frame rates Many game engines (especially the 3D ones), are variable frame rate. That means that they might run 30-60 frames per second depending upon how much drawing has to be done. To overcome this variableness (you don’t want your player running twice as fast on some machines), you will include the delta time (amount of time elapsed between two frames) included in the computation: if (KeyDown(DOWN))player.y+=SPEED * deltaTime; You will need to look in your game engines documentation to check what delta time is in your code. |
Simple velocity based movement
The next thing we think about it usually how to make a bullet/bomb/car move at a fixed speed in a direction. Normally we end up with code like this:
Sprite bullet;
...
const float SPEED=10;
bullet.y= -SPEED * deltaTime; // -SPEED as its going upAny this works provided all bullets/bombs/cars go in the same direction, but usually that’s not the case. Therefore we need to have a velocity variable added to our Sprite class (I’m going to assume its vx & vy for simplicity). And our code becomes:
Sprite bullet;
const float SPEED=10;
bullet.vx=0; // not moving left/rightbullet.vy= -SPEED; // moving up...
bullet.x = bullet.x + bullet.vx * deltaTime; // move by vxbullet.y = bullet.y + bullet.vy * deltaTime; // move by vy
Does this look familiar to you? How about this?
This is the standard equations of motion (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Equations_of_motion) or from your O-level/high-school physics text book.
Look at equation [2], and the code above:
bullet.x = 0 + bullet.vx * deltaTime; // move by vxs = ut + ½ 0 t2 [2]
// Simplify:bullet.x = bullet.vx * deltaTime; // move by vxs = u * t
Guess what? The physics stuff which you studied because you had to pass the physics paper is actually used in your game.
Comment: vx,vy verses vel.x, vel.y You might be using a game engine with a Vector2 or similar so instead of: bullet.x = bullet.vx * deltaTime; // move by vxbullet.y = bullet.vy * deltaTime; // move by vy You have: bullet.pos.x = bullet.vel.x * deltaTime; // move by vxbullet.pos.y = bullet.vel.y * deltaTime; // move by vy Or even: bullet.pos = bullet.vel * deltaTime; // move by vel The concept is the same, it’s just a matter of fitting it to the syntax/game engine. Remember, I’m selling concepts here, not exact code.
|
Comment: 1D/2D/3D All my examples here are 2D based (x,y), but the code work 100% the same for 3D (x,y,z) or even for 1D (if you wanted that). If there is anything which is different between 2D & 3D, I will mention it. |
Adding acceleration to our velocity based movement
Well if the physics stuff works with our velocity routines, we could also add in the acceleration routines. Lets assume the sprite class has an ax, ay for acceleration:
Sprite bullet;
const float SPEED=10;
const float GRAVITY=2;
bullet.vx=0; // not moving left/rightbullet.vy= -SPEED; // moving upbullet.ax=0; // no accelerationbullet.ay=GRAVITY; // gravity is down...
bullet.vx += bullet.ax * deltaTime; // apply accelerationbullet.vy += bullet.ay * deltaTime; // apply accelerationbullet.x += bullet.vx * deltaTime; // apply velocitybullet.y += bullet.vy * deltaTime; // apply velocity
Any there we have it. We launch our bullet, it goes up in the air, and then down again.
Comment: Gravity is not always 9.8 I’m sure a few of you looked at the code & said ‘gravity is not 2, its 9.8’. Sorry you are wrong. Gravity on earth is 9.8m/s, but this is not earth, this is a computer game. Our unit of measurement is not meters, its pixels (or some other abstract unit). You will need to fiddle with your SPEED/GRAVITY values until they are the right amount for your game. |
Adding direction to our velocity based movement
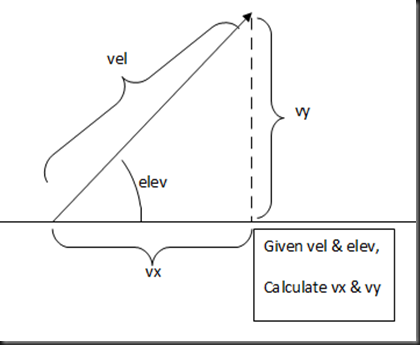
Ok, so a bullet up/down is rather boring, you probably want some kind of directional aiming (like a cannon trajectory), like this:
OK, well dust off your maths textbooks & answer me the following question:
“But Sir, this is maths!” I hear the cry.
Yes it is! Just like the physics we did earlier!
So get over it & solve it.
...
A bit of head scratching and sin/cosine laws later and we get:
vx = vel cos(elev) vy = vel sin(elev) |
Looking back over our code from earlier we could make the following changes:
const float GRAVITY=2;
const float VELOCITY=5;
const float ELEVATION=PI/2;
// bullet.vx=0; // not moving left/rightbullet.vx=VELOCITY * cos(ELEVATION);
// bullet.vy= -SPEED; // moving upbullet.vy=VELOCITY * sin(ELEVATION);
...
And ‘hey presto’, we have a moving object flying on a nice trajectory. All of a sudden all these math classes seem to have some use
Next Step: Space Flight
How much new stuff do you think you need to learn to move on to asteroids?
Well, pretty much nothing new. It’s just a matter of applying it in a slightly different context.
So here is our basic idea:
The player has a position, a velocity and a rotation. When the press the forward key, it will generate a thrust (acceleration) in whichever direction the player is facing right now. The original asteroids game often did not include a deceleration (drag), but we can add it in later if we chose to.
So here is our basic code:
Sprite player;
const float SPEED=10, TURN_SPEED=PI/2;
player.position=...; // set initial positionplayer.angle=0; // no angleplayer.velocity=Vector2(0,0); // no velocity...
if (KeyDown(LEFT)) player.angle-=TURN_SPEED * deltaTime;if (KeyDown(RIGHT)) player.angle+=TURN_SPEED * deltaTime;if (KeyDown(THRUST)){Vector2 accel;
accel.x= SPEED * sin(player.angle);
accel.y= SPEED * cos(player.angle);
player.velocity += accel * deltaTime;
}
player.position += player.velocity * deltaTime;
Comment: Introducing Vector2 I’m getting a little tired of x+= vx; y+= vy; So I’m going to assume some kind of class (Vector2) which holds an X & Y parameter that supports the basic arithmetic operation (+ - * /). Otherwise this code is going to get more and more tedious. |
Take note how, when the player presses thrust the velocity changes. But the movement happens regardless of whether the player is thrusting or not. This means that once the player begins moving, they will never stop. The player can only stop if they deliberately turn to face the opposite direction and thrust to stop themselves. This is accurate physics, but not necessarily good for our game.
Comment: Accuracy vs Playability A key thing to remember in all games is we are aiming for fun, not realism. When I used to play counter-strike in the LAN shop & used to get annoyed at the expert players who would jump out of second floor windows, shooting as they fell & kill me. Or the players who would be continually jumping all over the place while shooting me. |
Adding a slowdown: Drag
Now back on topic: lets add in some kind of friction to slow the player down. Actually without some kind of drag it would be possible for the player to reach infinite speed, since they can accelerate forever in one direction. The drag also allows the player who doesn’t press a key to eventually come to a stop. It’s actually quite simple to do:
Sprite player;
const float SPEED=10, TURN_SPEED=PI/2, DRAG=0.01f;
...
if (KeyDown(THRUST)){...
}
player.velocity -= player.velocity * DRAG * deltaTime; // dragplayer.position += player.velocity * deltaTime; // move player
The basic idea here is that, there will always be a bit of drag to slow the player down. The drag is proportional to the players speed. If the drag is 1/10 that’s quite a bit of friction & it will slow down fast. If its 1/1000 that’s very little and will only slow eventually. If the friction is 0.5 or even 1.0, then the object will hardly move at all.
I think the top speed should be SPEED/DRAG, but check it in your game to see how it works & adjust the factors to fit your need.
Conclusion
That’s our basic movement. It was only 2D, but the 3D version is just the same. That’s enough for basic gameplay.
Happy Coding:
Mark